Revolutionizing Large Language Model Training: The Era of Weight Streaming and Wafer-Scale Architectures
Introduction: The Hardware Bottleneck in the Age of Generative AI
The landscape of artificial intelligence is currently defined by a relentless pursuit of scale. As we digest the latest GPT-4 News and look toward the horizon of GPT-5 News, one technical reality becomes increasingly clear: the traditional hardware architectures that brought us here are hitting a wall. The sheer size of modern Large Language Models (LLMs)—spanning hundreds of billions to trillions of parameters—has turned GPT Training Techniques into a complex logistical puzzle involving thousands of GPUs and intricate software orchestration.
For years, the GPT Ecosystem has relied on distributed computing clusters where the model is split across many chips. This approach, while effective, introduces significant inefficiencies regarding memory bandwidth, communication latency, and code complexity. However, recent GPT Architecture News highlights a paradigm shift: the emergence of weight streaming and wafer-scale architectures. This innovative approach promises to decouple memory from compute, allowing for linear scaling without the need for complex model parallelism. As we explore OpenAI GPT News and the broader industry trends, it is essential to understand how these architectural breakthroughs could democratize access to GPT Custom Models News and accelerate the development of next-generation AI.
Section 1: The Scaling Challenge in Traditional GPT Architectures
To appreciate the significance of weight streaming, we must first understand the limitations of the status quo. Current GPT Models News often focuses on the capabilities of the models, but the engineering required to train them is equally newsworthy. In a traditional GPU cluster, memory is coupled with compute. Each chip has a finite amount of high-bandwidth memory (HBM). When a model like those found in ChatGPT News exceeds the memory capacity of a single chip, engineers must employ complex strategies.
The Complexity of Model Parallelism
When a model is too large for one device, it must be sliced up. This is known as model parallelism. There are two primary forms:
- Pipeline Parallelism: Different layers of the neural network are placed on different GPUs. Data flows through them in a sequence.
- Tensor Parallelism: Individual mathematical operations (matrix multiplications) are split across multiple GPUs.
While these techniques enable the training of massive models, they require significant code modification. This complexity acts as a barrier to entry, limiting GPT Fine-Tuning News and GPT Research News to only the most well-funded tech giants. Furthermore, as GPT Scaling News indicates, the communication overhead between these GPUs slows down the training process, reducing overall GPT Efficiency News.
The Memory Wall
The “Memory Wall” refers to the disparity between processor speed and the speed at which data can be moved to the processor. In GPT Hardware News, this is the defining bottleneck. Even if a processor can perform quadrillions of operations per second, it sits idle if it is waiting for weights to be loaded from memory. This latency impacts everything from GPT Inference News to GPT Latency & Throughput News, making real-time applications in GPT Gaming News or GPT Finance News more difficult to implement cost-effectively.
Section 2: Weight Streaming and Data Parallelism
The latest GPT Architecture News suggests a move away from splitting the model. Instead, new hardware paradigms are focusing on “Weight Streaming.” This architecture fundamentally changes how data moves through the system, offering a solution that is “data-parallel only.”
How Weight Streaming Works
In a weight streaming architecture, the model weights are stored in an external, massive memory bank rather than on the chip itself. During training or inference, these weights are streamed onto the compute wafer layer by layer. The compute engine performs the calculations for that layer across a batch of data, and then the weights are streamed off to make room for the next layer.

This approach has profound implications for GPT Optimization News. Because the weights are not static on the chip, the chip’s on-board memory can be dedicated entirely to activation data. This allows the hardware to process massive batch sizes, which is a key factor in stabilizing training for large models.
The End of Model Partitioning
The most revolutionary aspect of this architecture is the elimination of model partitioning. Because the weights are streamed, the hardware treats a trillion-parameter model exactly the same way it treats a billion-parameter model. The software does not need to know how to split the model across chips. This means researchers can scale from GPT-3.5 News sized models to massive GPT Future News architectures without changing a single line of model code. This simplification is a game-changer for GPT Code Models News and developers working on GPT APIs News.
Wafer-Scale Computing
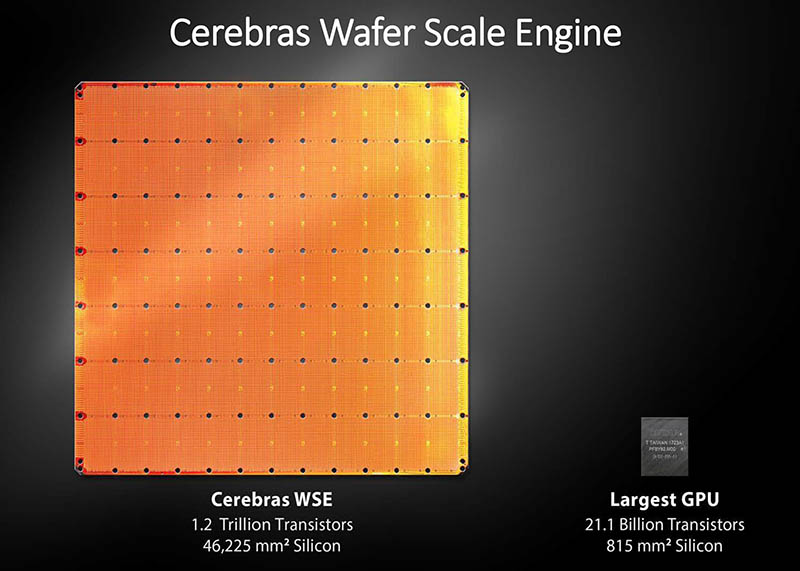
To make weight streaming effective, you need massive compute density. This is where wafer-scale engines come into play. Instead of cutting a silicon wafer into hundreds of individual chips, the entire wafer is used as a single processor. This provides unprecedented bandwidth and core counts, allowing the weight streaming mechanism to operate without stalling. This level of integration is vital for GPT Multimodal News, where models must process text, images, and audio simultaneously, requiring immense throughput.
Section 3: Implications for the GPT Ecosystem and Industry
The shift toward weight streaming and wafer-scale systems is not just a hardware curiosity; it reshapes the entire GPT Ecosystem News. By lowering the barrier to training large models, we can expect a surge in specialized applications across various sectors.
Democratizing High-End Training
Currently, GPT Competitors News is dominated by a few players because the infrastructure required to handle model parallelism is so expensive and complex. With data-parallel only architectures, organizations can train large models simply by adding more data. This will accelerate GPT Open Source News, as smaller labs and universities will be able to contribute meaningfully to the state of the art without needing clusters of thousands of GPUs.
Impact on Vertical Applications
GPT in Healthcare News: Medical data is highly private and complex. Hospitals often cannot send data to public APIs due to GPT Privacy News and GPT Regulation News. Easier training architectures allow healthcare institutions to train proprietary, HIPAA-compliant GPT models on-premise using their vast datasets.
GPT in Legal Tech News: Law firms require models trained on specific case law and contracts. Weight streaming allows for efficient GPT Fine-Tuning News on massive legal corpuses, creating highly specialized GPT Assistants News for lawyers.
GPT in Education News: Educational institutions can train models on specific curriculums or pedagogical methods, creating personalized tutors that adapt to student needs without the latency issues discussed in GPT Inference Engines News.
Advancements in Multimodality and Agents

As we look at GPT Vision News and GPT Agents News, the models are becoming more complex, not just larger. Agents require long context windows and the ability to retain state. The memory advantages of weight streaming architectures allow for significantly longer sequence lengths, which is critical for GPT Applications News involving complex reasoning and multi-step tasks.
Section 4: Efficiency, Ethics, and Future Outlook
While the architectural advancements are promising, they bring new considerations regarding efficiency, ethics, and deployment strategies.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
GPT Efficiency News is increasingly focusing on the carbon footprint of AI. Traditional clusters burn vast amounts of energy moving data between chips. By keeping the data movement on a single wafer and streaming weights efficiently, these new architectures can offer better performance-per-watt. This is crucial for GPT Trends News, as the environmental impact of AI becomes a regulatory concern.
Sparsity and Compression
Weight streaming is particularly well-suited for exploiting sparsity—the idea that many weights in a neural network are zero and don’t need computation. GPT Compression News and GPT Quantization News are vital here. Advanced architectures can dynamically skip zero-value weights during the stream, resulting in linear speedups. This makes GPT Distillation News more relevant, as we can train massive sparse models and distill them into dense, smaller models for GPT Edge News deployment.
Ethical Considerations and Safety
With great power comes great responsibility. If training massive models becomes easier, GPT Safety News and GPT Bias & Fairness News become even more critical. Lower barriers to entry mean that malicious actors could also train powerful models for disinformation or cyberattacks. The GPT Ethics News community must develop robust frameworks for GPT Deployment News, ensuring that these powerful hardware capabilities are used responsibly.
Real-World Scenario: The Enterprise Shift
Consider a large financial institution analyzing GPT in Finance News. Currently, they might rely on GPT Plugins News or external APIs. However, with a weight-streaming appliance, they could train a 50-billion parameter model on decades of proprietary trading data overnight. This model would be secure, internal, and highly specialized, offering a competitive edge that generic GPT Chatbots News cannot match.
Best Practices for Adopting New Architectures
For organizations looking to leverage these advancements in GPT Architecture News, several best practices apply:
- Assess Data Parallelism Needs: Determine if your bottleneck is compute or memory. If you are struggling with partitioning logic, weight streaming is a strong candidate.
- Focus on Data Quality: Since the architecture handles the scaling, your primary lever for improvement becomes the dataset. GPT Datasets News suggests that data curation is the new coding.
- Evaluate Inference Latency: For GPT Applications in IoT News, ensure that the inference engine supports the low latency required for edge devices.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes: Keep an eye on GPT Regulation News, as on-premise training offers a different compliance profile compared to using public APIs.
Conclusion
The evolution of GPT models is inextricably linked to the evolution of the hardware that powers them. The recent shift toward weight streaming and wafer-scale architectures represents a pivotal moment in GPT Architecture News. By eliminating the need for complex model parallelism and solving the memory wall, these technologies are set to accelerate the arrival of GPT-5 News and beyond.
From enhancing GPT Multilingual News capabilities to enabling hyper-specialized GPT in Marketing News applications, the democratization of training infrastructure will unlock value across every sector. However, as we embrace these tools, we must remain vigilant regarding GPT Safety News and GPT Ethics News. The future of AI is not just about bigger models; it is about smarter, more efficient, and more accessible architectures that empower GPT Creativity News and innovation on a global scale. As we move forward, the synergy between GPT Software and GPT Hardware News will define the next era of artificial intelligence.



